This is my 19th blog on Back to School (BTS) deals and ideas. In the last blog we saw some Cool and simple ideas to make Healthy School Lunches and Save Money. In this blog you will see a new study which shows that how proper doze of Vitamin D will keep your kids more healthy in long run.

What is Vitamin D?

Vitamin D is a steroid vitamin, a group of fat-soluble pro-hormones, which encourages the absorption and metabolism of calcium and phosphorous. People who are exposed to normal quantities of sunlight do not need vitamin D supplements because sunlight promotes sufficient vitamin D synthesis in the skin.
Forms of Vitamin D
Five forms of vitamin D has been discovered, vitamin D1, D2, D3, D4, D5. The two forms that seem to matter to humans the most are vitamins D2 (ergo-calciferol) and D3 (chole-calciferol)

Sunlight and vitamin D requirements
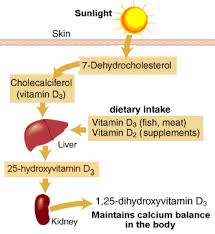
If you live in the tropics and can expose your unprotected skin to two sessions of 15 minutes of sunlight each week your body will naturally produce adequate amounts of vitamin D. The following factors may reduce your body's vitamin D synthesis:
If you live far from the equator, your sunlight exposure will be less during many months of the year.
Cloud cover
Smog
Sunscreens
If your body cannot produce enough vitamin D because of insufficient sunlight exposure you will need to obtain it from foods and perhaps supplements. Experts say that people with a high risk of vitamin D deficiency should consume 25 μg (1000 IU) of vitamin D each day so that there is a good level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in the bloodstream. Elderly people, as well as people with dark skin should consume extra vitamin D for good health.
How much vitamin D do I need?

The information below relates to people who do not have exposure to sunlight.
According to the Food Nutrition Board at the Institute of Medicine of The National Academies, which created the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs), people should be in taking the following amounts of vitamin D if nothing is being synthesized (no sunlight exposure):
Children up to 13 years - 5 mcg (200 IU)
14-18 years - 5 mcg (200 IU)
19-50 years - 5mcg (200 IU)
51-70 years - 10 mcg (400 IU)
71+ years - 15 mcg (600 IU)

Sources of Vitamin D

The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that exclusively or partially breastfed babies should receive supplements of 400 UI per day shortly after birth, and when they are weaned they should consume a minimum of 1,000 mL/day of vitamin D fortified formula or whole milk. Non-breastfed infants consuming less than 1,000 mL/day of vitamin D-fortified formula or milk should receive a vitamin D supplement of 400 IU per day. It also recommends that older children and adolescents who do not get 400 IU per day through vitamin D fortified milk and foods should take a 400 IU vitamin supplement each day

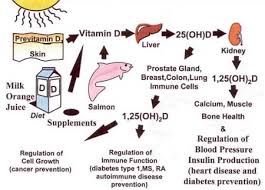
Benefits of Vitamin D
- It is crucial for the absorption and metabolism of calcium and phosphorous, which have various functions, especially the maintenance of healthy bones.
- It is an immune system regulator.
- It may be an important way to arm the immune system against disorders like the common cold, say scientists from the University of Colorado Denver School of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital and Children's Hospital Boston.
- It may reduce the risk of developing multiple sclerosis. Multiple sclerosis is much less common the nearer you get to the tropics, where there is much more sunlight, according to Dennis Bourdette, chairman of the Department of Neurology and director of the Multiple Sclerosis and Neuro-immunology Center at Oregon Health and Science University, USA.
- Vitamin D may have a key role in helping the brain to keep working well in later life, according to a study of 3000 European men between the ages of 40 and 79.
- Vitamin D is probably linked to maintaining a healthy body weight, according to research carried out at the Medical College of Georgia, USA.
- It can reduce the severity and frequency of asthma symptoms, and also the likelihood of hospitalizations due to asthma, researchers from Harvard Medical School found after monitoring 616 children in Costa Rica.
- It has been shown to reduce the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis in women.
- A form of vitamin D could be one of our body's main protections against damage from low levels of radiation, say radiological experts from the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene.
- Various studies have shown that people with adequate levels of vitamin D have a significantly lower risk of developing cancer, compared to people with lower levels. Vitamin D deficiency was found to be prevalent in cancer patients regardless of nutritional status, in a study carried out by Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
- Researchers at the University of Minnesota found that Vitamin D levels in the body at the start of a low-calorie diet predict weight loss success, suggesting a possible role for vitamin D in weight loss.
What foods have Vitamin D?

Vitamin D is not found in many foods; however, you can find vitamin D in:
•Cow’s milk
•Fortified soy and rice beverages
•Fortified orange juice
•Fatty fish like salmon and sardines
•Margarine
•Egg yolks
•Fortified yogurts (check the label)
Over the last few hundred years’ human lifestyles have changed. The industrial revolution resulted in more indoor work and less exposure to sunlight. Many societies around the world wore more clothing over the centuries, further reducing skin exposure to sunlight. These changes have brought with them a significant reduction in the natural production of vitamin D and subsequent diseases.
Countries responded to these changes by fortifying some foods with vitamins D2 and D3, examples include breakfast cereals, bread, pastries, oil spreads margarine, milk and other dairy products. Initially, some scientists complained that nutritional fortification and recommended supplementation doses were not making up for the shortfall. These people were ignored, and sometimes ridiculed - however, over the last few years studies indicate that they may have been right after all.
Not that many foods contain vitamin D. Some fish, such as salmon, tuna and mackerel, as well as fish liver oils are considered to be the best sources. Some vitamin D is also present in beef liver, cheese and egg yolks. Most of these are Vitamin D3. Some mushrooms provide variable amounts of vitamin D2.
Most of the food sourced vitamin D in the western diet comes from fortified foods - where vitamin D is artificially added. Most US milk is fortified with 100 IU/cup of vitamin D. In the 1930s milk was fortified in many countries to combat rickets, which was a major health problem then.
New Research-Study links sickest kids to low vitamin D levels

IN Canada we need more Vitamin D supplement as we do not get enough sun. In summer times if we get sun than we have another problem of UV. So we all really need supplement or food with vitamin D.
A new Canadian study of children hospitalized with severe infections shows three-quarters of them had low levels of vitamin D. Our bodies make this vitamin when our skin is exposed to spring or summer sunshine. It also comes in cheap pills, in baby formula and drops for breastfed infants. Canadians tend to have low levels of vitamin D because we live too far north to manufacture it for much of the year. Fall and winter sunshine is too weak. But the 300 young patients at the Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario and five other hospitals had low levels even by Canadian standards. And Dr. Dayre McNally noticed another tendency among them: the sickest children and teenagers in the hospitals were usually those with the lowest vitamin D levels. McNally, an intensive care physician, says most Canadian children need a vitamin D supplement, the dose depending on a person's age and weight. The study is published in the scientific journal Pediatrics.
McNally got started on vitamin D after a rheumatologist he knew found low vitamin D in children with unexplained joint and muscle pain. McNally then moved on to pneumonia, and eventually to a wide spectrum of illness in CHEO and other children's hospitals. Most were severe respiratory infections and blood infections. "We've known for 100 years that vitamin D was necessary for good bone growth," he said. A severe deficiency can cause rickets, or crooked bones, but children with rickets often have pneumonia too.

A lack of the "sunshine vitamin" may not matter much when a person is healthy, his research found. But once a person is sick, the deficiency makes it harder to recover. And it affects many organs and tissues in the body - heart, lungs, muscles and the brain. "They can get by with low vitamin D levels when things are going well, when you're on even ground. But when you're trying to climb the mountain, having low vitamin D levels is bad. Your heart goes, 'Oh geez, now I really miss you.' " He believes our bodies need vitamin D to recover from surgery as well as to heal an illness. In the youngest babies, a vita-min deficiency means their mothers were lacking vitamin D during pregnancy.
He says vitamin D doses in multi-vitamins for pregnant women are too low. Some infants were breastfed but not getting a vitamin supplement and some older children had been staying indoors, or covering up with long clothing or sunscreen. As well, vitamin D is added to milk but some children were likely missing it in their diet, he said. Canadian studies have shown that "compliance with vitamin D in infants and young children is terrible."
(Source- Scientific journal Pediatrics)
Similar report in US-Docs doubles kids' vitamin D recommendations in 2009
American Academy of Pediatrics suggests 400 units daily to fight disease.
CHICAGO — The nation's leading pediatricians group says children from newborns to teens should get double the usually recommended amount of vitamin D because of evidence that it may help prevent serious diseases. To meet the new recommendation of 400 units daily, millions of children will need to take daily vitamin D supplements, the American Academy of Pediatrics said. That includes breast-fed infants — even those who get some formula, too, and many teens who drink little or no milk. Baby formula contains vitamin D, so infants on formula only generally don't need supplements. However, the academy recommends breast-feeding for at least the first year of life and breast milk is sometimes deficient. Most commercially available milk is fortified with vitamin D, but most children and teens don't drink enough of it — four cups daily would be needed — to meet the new requirement, said Dr. Frank Greer, the report's co-author.
The new advice is based on mounting research about potential benefits from vitamin D besides keeping bones strong, including suggestions that it might reduce risks for cancer, diabetes and heart disease. But the evidence isn't conclusive and there's no consensus on how much of the vitamin would be needed for disease prevention. The new advice replaces a 2003 academy recommendation for 200 units daily. That's the amount the government recommends for children and adults up to age 50; 400 units is recommended for adults aged 51 to 70 and 600 units for those aged 71 and up. Vitamin D is sold in drops for young children, capsules and tablets.
No comments:
Post a Comment